Heavy Equipment
7 Types of Excavators
A list of different types of excavators and their uses.

Excavators are earthmoving vehicles that are fitted with a revolving cab, arm, boom, bucket, and rotating tracks or wheels. They are a common sight in construction sites.
Different types of excavators are used to perform various construction and engineering tasks – from highway construction to mining and demolition of condemned buildings.
Here are seven popular types of excavators.
1. Crawler Excavators
Hailed as the ultimate digging tool, crawler excavators – also known as standard excavators or compact excavators – are an integral part of any heavy construction work.
A crawler excavator is easily identifiable because it runs on two rotating tracks instead of wheels – more or less the way a military tank does.
It is mainly used in heavy-duty construction jobs.
Crawler excavators are designed to dig, pick and move debris and are mainly used in the excavation of foundations, trenches and holes.
They are also used for dredging, grading, landscaping and demolition.
The machines use hydraulic power mechanisms to lift heavy debris on site.
Although slower than wheeled excavators, the tracked chassis of crawler excavator types make them more stable and ideal for sites located in areas with uneven terrain.
RELATED: Most Powerful Road Construction Equipment
Other attachments can be incorporated to adapt the crawler into a crushing, boring, grappling, lifting and cutting machine hence increasing its usefulness at the work site.
2. Wheeled Excavators
Wheeled excavators are designed to operate like crawler excavators only that they are fitted with wheels instead of tracks.
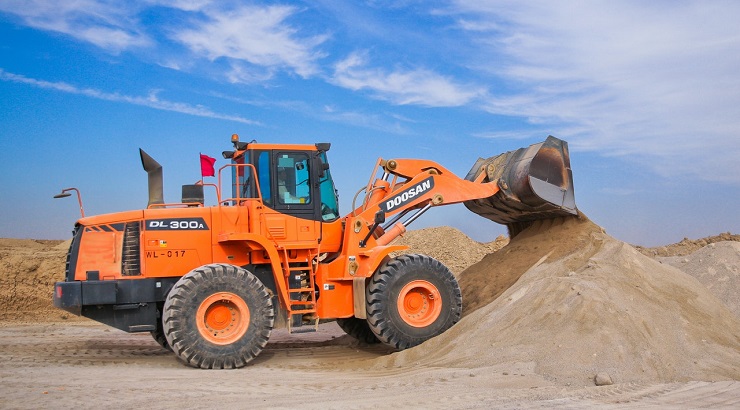

They are faster than crawler excavators and can easily move on asphalt or concrete.
Since they have less traction than crawler excavators, these types of excavators are unsuitable for sites with uneven terrain as well as places with soft soils or mud.
3. Dragline Excavators
These types of excavators come in huge sizes and are designed to operate differently.
They use a hoist rope system and a dragline to elevate and lower buckets and drag them toward the driver. With a digging depth of 65 meters, dragline excavators are ideal for excavating underwater.
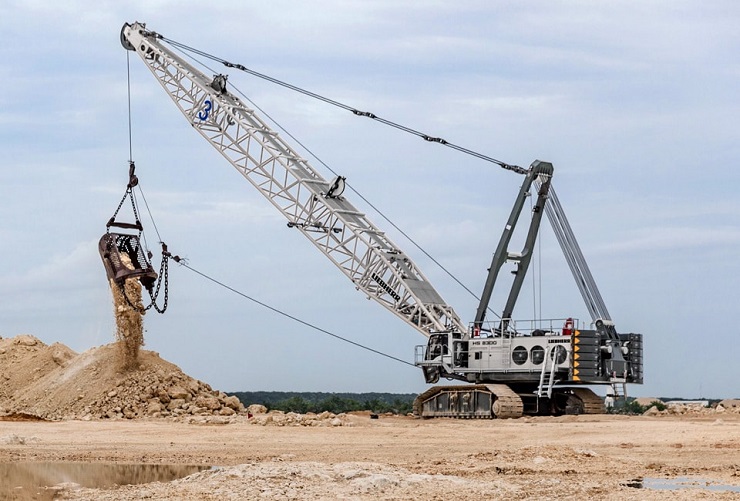

These machines are mainly used for surface mining, deep pile driving, harbor construction, road excavation, and massive underwater operations.
Owing to their bulkiness, dragline excavators are often assembled on-site.
4. Skid Steers
Unlike typical excavators, skid steers are fitted with booms and buckets that face away from the operator – enabling the attachment to reach over the cab instead of around it.
This makes them ideal for narrow areas or sites with limited spaces.

Skid steers are often used for small tasks such as site cleaning, debris removal, digging pools, etc., where space is limited thus requiring tricky manoeuvres.
5. Suction Excavators
Also known as vacuum excavators, suction excavators are fitted with a suction pipe that functions in the same way as a pressure vacuum.
RELATED: Top 10 Excavator Companies
With the help of a built-in water jet, the suction system sucks up soil and debris at speeds of 200 miles per hour. A suction excavator is often used for precise digging jobs as it reduces the chances of cracking.
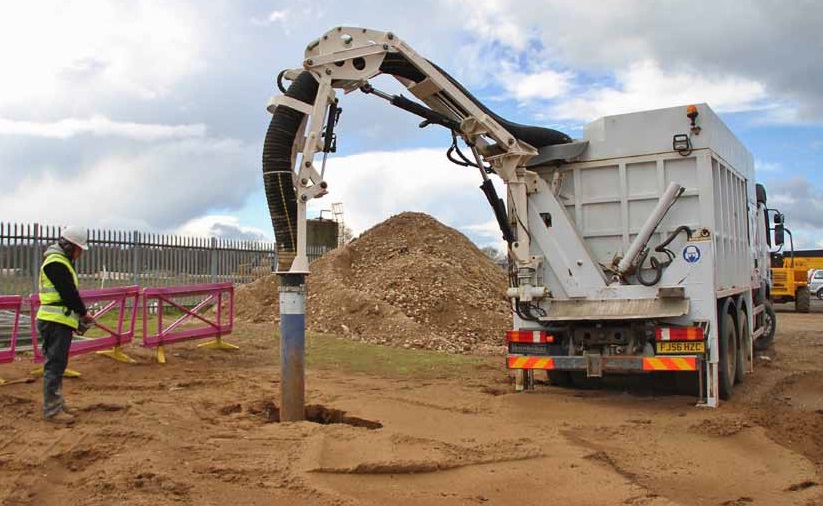

One of the main disadvantages of suction excavators is that the suction pipe is usually 30 centimetres or less in diameter, which makes them unsuitable for large-scale projects.
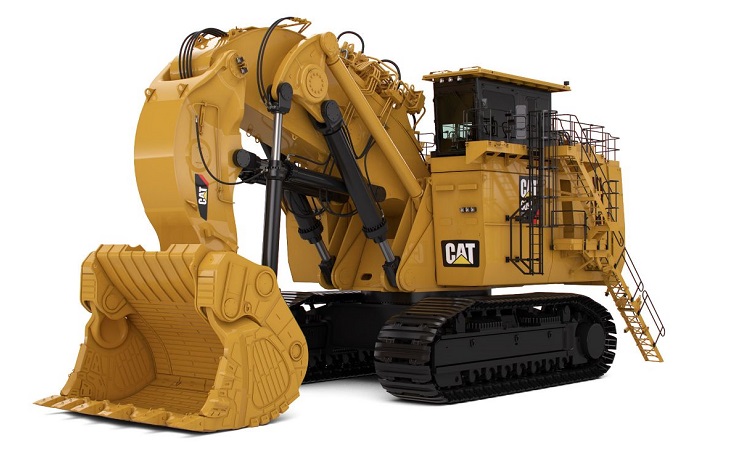
6. Hydraulic Shovels
Also known as power shovels, hydraulic shovels are the most powerful types of excavators.
They come with a powerful engine and large buckets that make them ideal for mining and heavy-digging jobs. However, the diggers are often larger than necessary for most jobs.

7. Long Reach Excavators
These types of excavators are fitted with a lengthier arm and boom compared to standard excavators to allow them to excavate hard-to-reach sites.
In most cases, the long-reach excavator is fitted with an extendable arm that can reach 40 to 100 feet away to allow delicate and hazardous excavation from a safe distance.
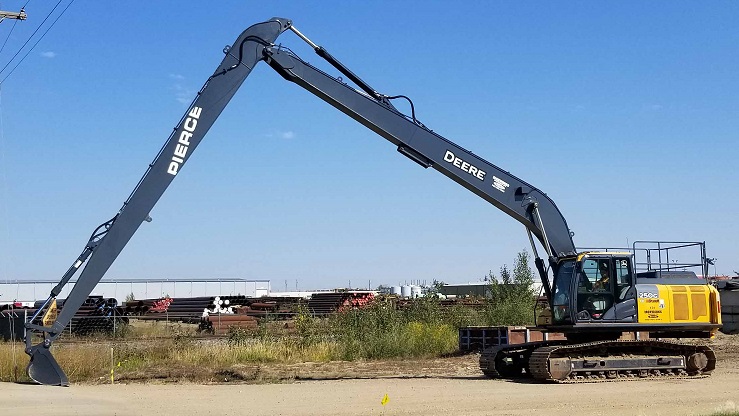

Long-reach excavators are suitable for projects where the terrain or site prevents the machine from moving too close – for example, demolition sites over a water body.
Different attachments can be fitted to the extendable arm to perform other tasks such as crushing, and shearing. However, the long arms make it impossible to operate in tight spaces.