Features
How to Pick the Right Trench Box for Your Project
A review of various trench boxes, their uses, types, and selection tips.
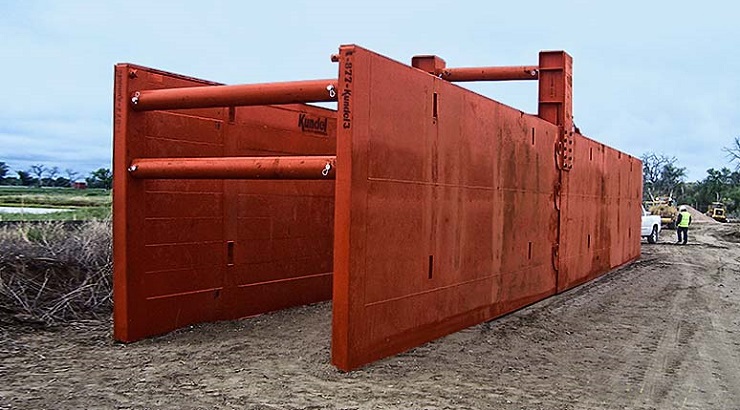

In excavation, keeping workers safe in trenches is essential. One key tool for this purpose is the trench box, which is also known as a trenching box or box trench.
A trench box is a steel or aluminium structure designed to secure the sidewalls of a trench or excavation to prevent a collapse.
This article covers everything you need to know about trench boxes, including tips on selecting the right trenching box for your project.
Types of trench boxes
There are essentially four different types of trench boxes.
Heavy-duty steel boxes: These trench boxes have thick, high-strength steel walls and reinforced frames for superior protection in tough excavation environments.
Lightweight steel boxes: These trench boxes have thinner steel walls and lighter frames to offer protection in less challenging excavation environments. They are suitable for small excavation jobs or where ease of use is prioritised.
Aluminum trench boxes: These trench boxes are made of lightweight aluminium to offer protection in moderate excavation environments. They are easy to transport and assemble, making them ideal for small projects and quick setups.
RELATED: How to Prevent Deadly Construction Accidents
Modular trench boxes: Made of replaceable panels and components, these trench boxes can be configured according to specific job requirements. They are suitable for projects requiring frequent adjustments or varying trench sizes.
How to pick the right trench box
Considerations when selecting a trenching box:
Budget: Balance the initial cost of a trench box with its durability and maintenance needs. While heavy-duty boxes may have higher upfront costs, their durability can lead to savings over time as they require less frequent repair.
Jobsite requirements: Consider trench depth and width, soil type, and job site conditions. Heavy-duty boxes are ideal for deep excavations. Composite solutions suit deeper applications, while lightweight boxes are ideal for shallower trenches.
Compatibility: Make sure your equipment can handle the trench box. If you are using a big trenching box, you will need stronger machines, so double-check this.
Specifications: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for safe use in case of doubt. This includes determining workload limits, following installation instructions, and adhering to the recommendations for various applications.
How to use a trench box
Placement and installation:
Trench boxes should be placed in the trench with a suitable machine.
Set the box no more than 2 feet (0.6 metres) from the bottom of the trench for maximum protection.
RELATED: How to Prepare a Construction Site Safety Plan
Stacking boxes:
In the event of deep trenches, boxes can be laid on top of each other. Just make sure the boxes are tightly fitted to avoid movement.
Worker safety:
Workers should not be inside the trench box while it is being installed, removed, or moved vertically.
A ladder must be installed within 25 lateral feet of all workers and extend at least 3 feet (0.9 metres) above the top of the trench for safe access and exit.
Regular inspections:
Inspect trench boxes regularly for any signs of damage or wear, such as bends or deformities.
Follow the manufacturer’s tab data, which includes critical information like plate types, restrictions on lateral movement, and allowable loads.
Excavated materials:
Place excavated materials at least 2 feet (0.6 metres) away from the edge of the excavation to prevent them from falling back into the trench.
Safety tips
Trenches 1.5 metres deep must have a protective system.
Trenches over 1.2 metres deep need a ladder for entry and exit.
Ladders should extend at least 0.9 metres above the trench.
Place excavated materials at least 0.6 metres away from the trench edge.
FAQs
At what depth is a trench box required?
Trenches 1.5 metres or deeper require a protective system unless they are completely carved into stable rock. For shallower trenches, an expert may assess whether a protective system is necessary.
What are the benefits of trench boxes?
During excavations, trench boxes serve to avert the collapse of the excavated wall faces, ensuring the safety of workers from potential injury or fatality. Trench boxes also improve project efficiency, offering various time-saving advantages.
What’s the 5-4-3-2-1 rule excavation?
Trenches deeper than 5 feet (1.5 metres) need a protective system.
Those over 4 feet (1.2 metres) require a ladder extending at least 3 feet (0.9 metres) from the excavation.
Keep excavated materials 2 feet (0.6 metres) away from the edge, and keep 1 foot (0.3 metres) distance from heavy equipment to avoid damage or collapse.