Innovation
The A to Z of Modular Construction
The first instance of modular construction came in the 1830s.

What’s modular construction?
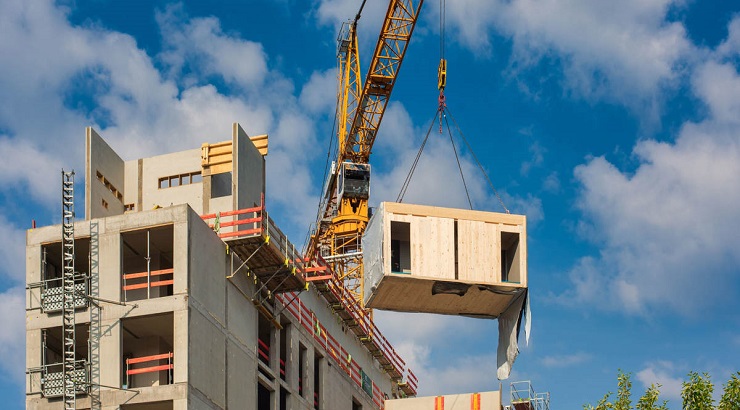
Modular construction is a process whereby a building is constructed off-site in a factory setting and then transported to the site for assembly.
In this mode of construction, building components are prefabricated in a factory as separate modules or units. Later on, the modules are transported to a construction site and assembled to form an integral structure.
By doing this, it can help reduce the construction schedule by up to 50%.
The reasons for its popularity in recent times are the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and quality control offered by modular construction.
It is particularly useful for projects where faster completion time is needed. Application includes residential, commercial, and other types of buildings.
When did modular construction start?
Although it recently gained popularity, modular construction has been around for so many years.
Indeed, the very first case of modular construction ever recorded dated back to the 1930s, when a British carpenter named John Manning prefabricated a house for his son. This house was constructed partially before being shipped to Australia for assembly.
Modular construction made a big hit during the California Gold Rush of the 1840s.
The style was also used in the construction of the iconic ‘Crystal Palace’ built for Britain’s Great Exhibition of 1851.
It further gained momentum in the shape of prefabricated structures during and after the Second World War.
How does modular construction work?
The process of modular construction involves buildings being manufactured in separate modules away from the building site and then transported to the site for integration.
A large part of the building, typically between 60–90%, is constructed in a factory either as an entire structure or as modular subassemblies for larger projects.
Off-site construction allows for the effective application of lean manufacturing techniques to produce high-quality prefabricated modules.
These are then joined together at a construction site by using inter-module connections that strongly secure the units and form a unified building.
RELATED: America’s 10 Finest Prefabricated Homes
Permanent modular buildings are designed to meet and, in most cases, go beyond the standards of conventional site-constructed homes; therefore, quality control is very strong, and higher levels of craftsmanship are available.
Can modular homes be moved?
Yes, one of the advantages associated with modular homes is their ability to be moved. However, it should be noted that not all types of modular buildings are designed to be moved. Only a specific type called ‘relocatable’ buildings is designed for relocation.
On the other hand, some modular homes are permanently attached to a foundation and these houses are not designed to be relocated. This kind of house, when assembled and anchored to a foundation is not supposed to be moved.
To answer this more in detail, let’s go back to the two general types of modular construction.
Types of modular construction
There are two kinds of modular construction: Relocatable Building and Permanent Modular Construction.
Relocatable Building – RBs are designed to be used again and again at multiple sites. They are perfect for schools, construction site offices, and medical clinics–any situation requiring temporary space solutions.
These buildings are designed for easy relocation, low-cost reconfiguration, quicker depreciation schedules, and excellent adaptability.
Unlike permanent structures, relocatable buildings are not permanently fixed to real estate but are installed per the manufacturer’s installation guidelines and local building codes.
Permanent Modular Construction – PMC is a sustainable construction process that uses offsite, lean manufacturing techniques to prefabricate single- or multi-story buildings in deliverable module sections.
PMC modules provide permanent solutions because they can be combined inconspicuously within site-built projects or stand alone as self-contained, fixed structures.
These modules are delivered with MEP, fixtures, and interior finishes within a short time.
Through this method, wastage of materials will be minimized, and better quality control can be attained than the projects that are carried out with traditional building procedures.
Is modular construction cheaper?
Several studies have proved that modular construction can assure a considerable amount of cost savings when compared with traditional on-site construction.
This is attributed to various factors, including weather conditions not affecting the project schedule and the ability to construct the structures offsite, which ensures reduced material wastage.
However, it is essential to note that the extent of such savings is likely to differ with different projects based on their characteristics, location, and complexity of the design, among others.
Therefore, it is highly recommended to make a detailed cost analysis considering the needs of your project to be sure whether modular construction is the best way forward.
How sustainable is modular construction?
Yes, modular construction is a sustainable method of construction. This process is efficient with less waste of raw materials being generated.
Energy efficiency realized from factory building drives down energy consumption; thus, modular construction can be termed green.
RELATED: 10 Construction Industry Trends to Watch This Year
Moreover, because of reduced site disturbance and transportation efficiency, with modular construction, this mode of construction propagates sustainability.
Pros and cons of modular construction
Modular construction is replete with several advantages over the traditional construction techniques. These advantages are:
- Faster construction: Because the modules would be constructed before on-site preparations, the time needed for construction becomes faster.
- Reduced material waste: Material supplies are better regulated in a factory, reducing the chances of material waste with a lesser impact on the environment.
- Enhanced quality and comfort: Factories offer better working conditions to produce better quality products, whereas workers enjoy a much more comfortable workplace.
- Efficient insulation: Many modular units use S.I.P.s for better thermal insulation and damp resistance than timber. Factory construction reduces moisture, significantly enhancing product quality.
- Flexibility: Modular structures can be easily added to over time or treated as relocatable buildings, ready for overhaul to meet new needs.
- Suitable for remote locations: Modular construction is ideal for remote areas where building may be very complicated or expensive.
- No weather delays: Construction delays due to adverse weather and onsite issues are eliminated as the modules are manufactured in a factory.
- Durability: Because modular units must meet the requirements for over-the-road travel and assembly, it is a more rugged construction than an on-site building.
- Time and cost savings: This alternate method of construction will allow one to save 30–50% of construction time over traditional methods, which equates directly to substantial cost savings.
However, modular construction has some key issues to consider, including:
- Logistical hurdles: The delivery of completed modules to the site is complex and requires careful management and, therefore expensive.
- Size limitations: There may be restrictions to the size of individual modules as a function of the manufacturing and/or transportation processes. Consequently, the dimensions of various rooms within the building may dictate or influence the building design.
Even in the light of these odds, modular construction would still hold great potential in many projects, having a set of solutions that are forever changing with the times.